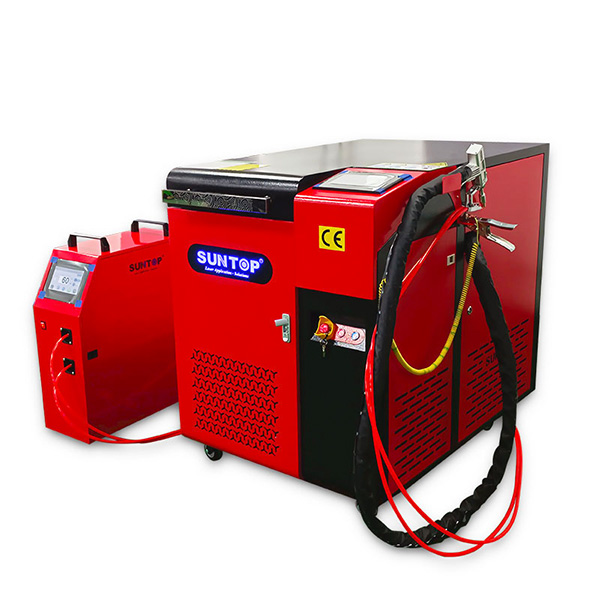
Handheld laser welder offer multiple significant advantages due to their unique design and technology, making them widely adopted in the welding industry.
1. Flexibility and Mobility
● Suitable for diverse work environments and scenarios
The lightweight design of handheld laser welding machines enables flexible operation across various work settings—whether on factory production lines, in repair workshops, or at customer sites—meeting welding demands with ease. This mobility makes them an ideal choice for diverse engineering requirements.
● Capable of maneuvering in confined or irregular spaces
Traditional welding equipment often requires substantial operating space, whereas handheld laser welding machines can easily access tight, hard-to-reach areas. For instance, when welding complex mechanical components or structures, operators can freely adjust welding angles as needed to achieve precise welds.

2. High Precision and Welding Quality
● Achieves Detailed and Consistent Welding Results
Leveraging the laser's high energy concentration, handheld laser welders can weld within extremely small areas, producing high-precision welds. This results in finer welds with smooth surfaces, requiring little to no post-processing.
● Minimizes Heat-Affected Zone and Reduces Material Deformation
Laser welding produces a relatively small heat-affected zone, effectively minimizing material deformation and thermal distortion. This advantage is particularly valuable in applications demanding exceptional weld quality, ensuring the structural integrity and strength of the welded components.
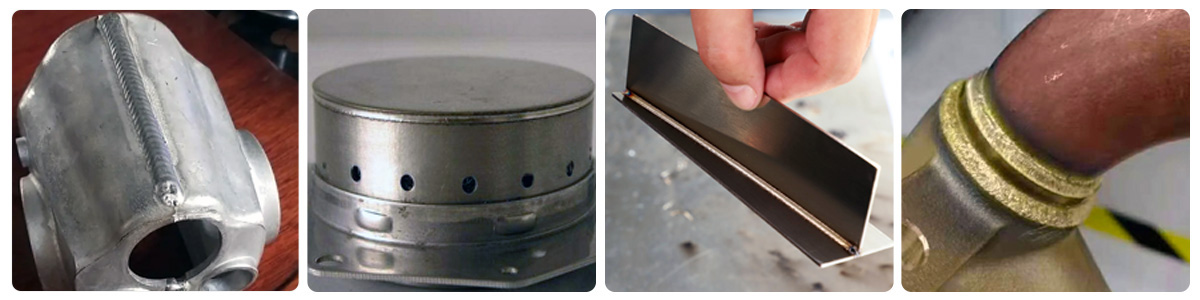
3. High Adaptability
● Capable of Welding Diverse Materials (e.g., Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Copper)
Handheld laser welding machines offer broad material adaptability, capable of joining diverse metallic materials. This capability makes them suitable for various industries, including automotive manufacturing, electronics, and pipeline construction.
● Handles materials of varying thicknesses
Whether working with thin sheets or thicker metal components, handheld laser welding machines can adjust laser parameters as needed to meet welding requirements for different thicknesses. This flexibility enables outstanding performance across diverse application scenarios.
With its flexibility, high precision, and strong adaptability, the handheld laser welding machine has become a vital technological tool in modern welding. It not only enhances welding efficiency and quality but also broadens the scope of welding applications, meeting the current market demand for diverse and customized welding solutions. Click here for more information






























































